meet gizmo, my tin toy robot gpt

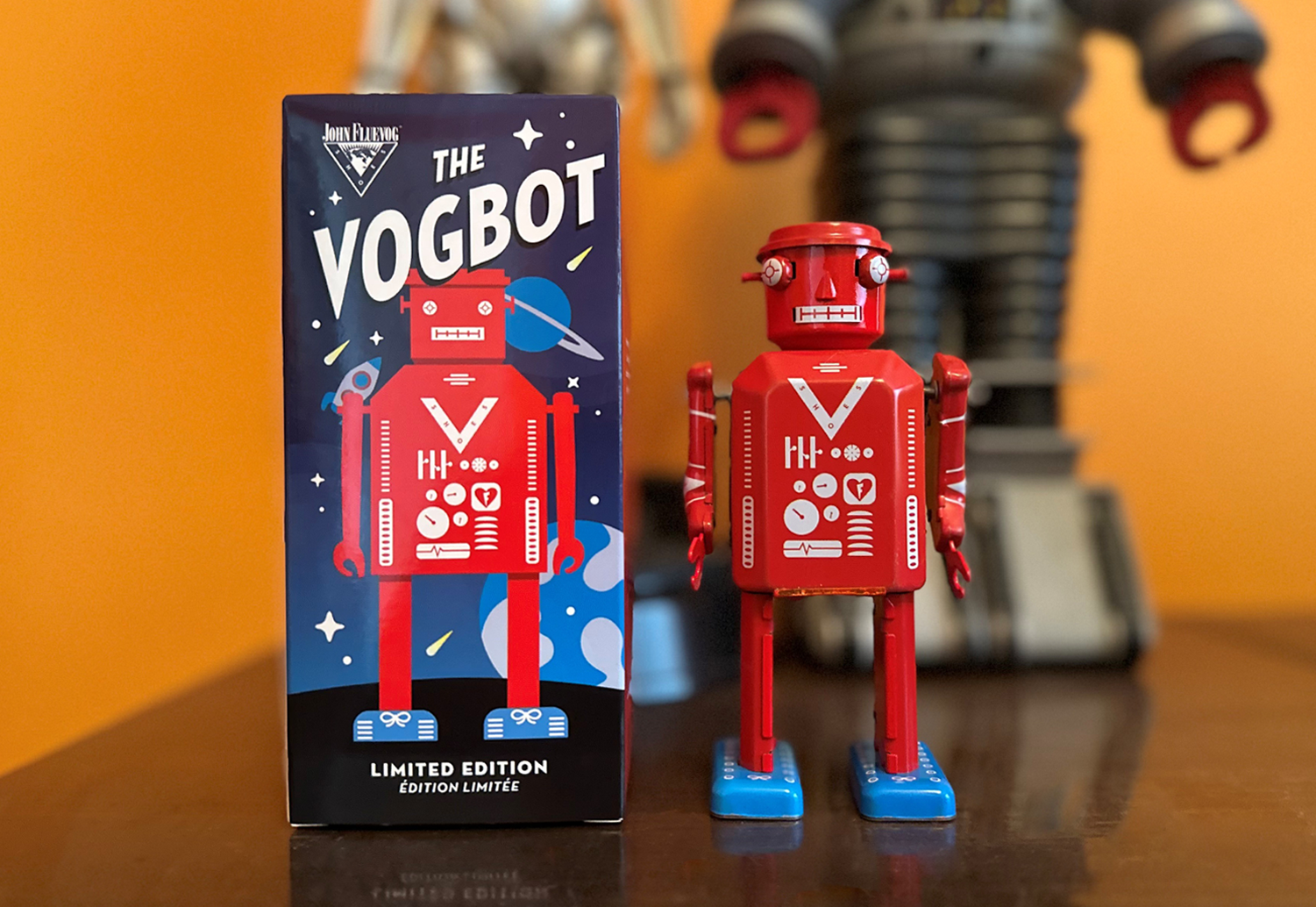
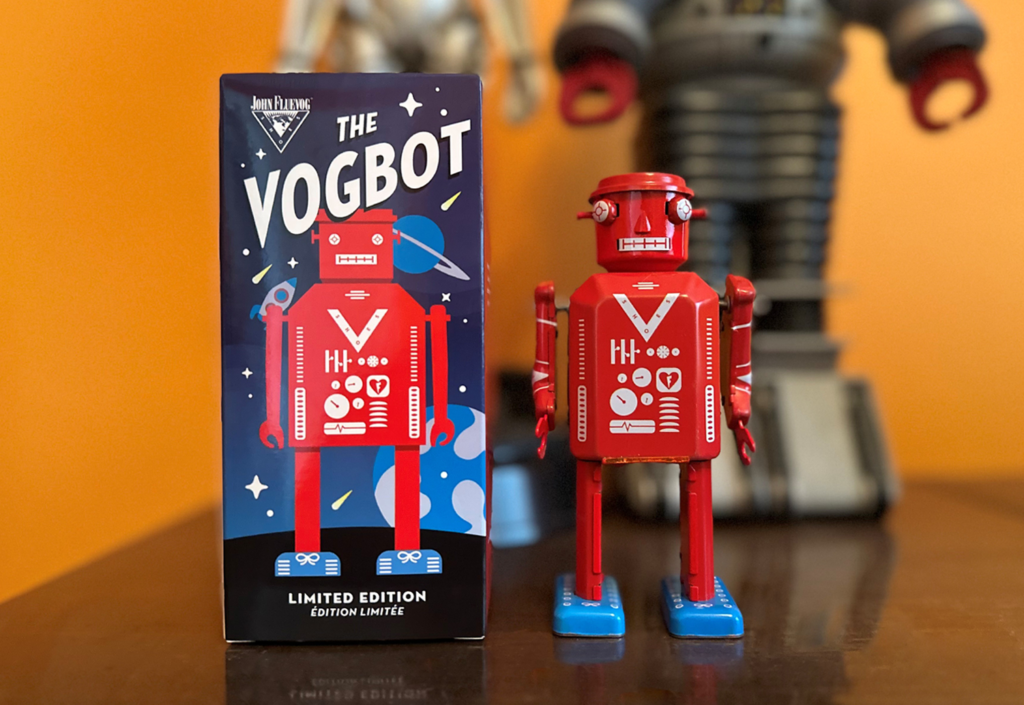
Left to right: early test renders of a robot, box design, and logo sheet, based on my design briefs, and generated by my custom GPT
For those who know me, you probably already know I’m an afficionado of the mid-century Japanese sci-fi tin toy design aesthetic, particularly robots. Last year, I built thirty bots in Blender that paid tribute to some famous examples of vintage Japanese tin robot designs, depicted in their original, showroom new glory. My goal after that was to diverge from these originals in my subsequent designs, imagining alternatives and nonexistent mashups that effectively extend the mid-century tin toy robot legacy in a theoretically alternate reality.
The Artist/AI Conundrum
Around that same time, I began experimenting with the relatively new frontier of generative AI imaging, testing out Midjourney, DALL·E, and Stable Diffusion. I was impressed by both the speed and variety of visuals I could generate with a well-crafted prompt – but something was missing from those early experiments: me.
While I tried in earnest to write prompts that reflected my personal design aesthetic, the outputs just didn’t “feel” like anything I would ever create by hand, using the tools I’m most accustomed to (pencils, markers, Blender, Photoshop, Illustrator, Procreate, etc.). Nonetheless, I wanted to figure out how to best integrate these impressive new technologies into my evolving creative process. Where – and how – does the power of AI converge with the originality, concepts, and outputs of the artist? And more immediately: how might this translate into my next set of Blender 3D robot interpretations, which are already digital to begin with?
Meet Gizmo, My Custom Tin Toy Robot GPT
Early last month, I bit the bullet and subscribed to ChatGPT Plus, ostensibly to help me track progress on personal design projects, improve quality of life workflows, and generally learn the ins and outs of collaborating with an AI agent more deeply. Looking back, it turned into a month full of surprises (which I’ll explore more in a separate post).
At one point, I told my chatbot (I call it Uran, after Astro Boy’s younger robot sister) about my idea to expand the universe of vintage tin toy robots with new creations. Uran suggested I consider making a custom GPT, an AI dedicated to a specific task or interest. I’d heard of them before, but figured it would be too technical. Uran assured me it would be easy to set up, and over the next 30 minutes, walked me step-by-step through building my first custom GPT, dedicated entirely to creating mid-century tin toy robots. Much easier than I anticipated.
I named it Gizmo, and immediately noticed how its personality contrasted with Uran’s. While both were helpful and friendly, Gizmo was laser-focused on a single mission: to help me extend the legacy of vintage robots in my personal design style.
Feeding the Machine: Design Briefs
To make a custom GPT “smarter” about a subject, you can upload files to its internal knowledge base, documents it references to inform its responses. I began by uploading my previous Blender 3D renders of tin robots individually, but quickly hit the 20-file limit. I realized that by compiling my references into multi-page PDFs, I could bypass the limit entirely.
So I created five custom design briefs in InDesign and exported them as PDFs:
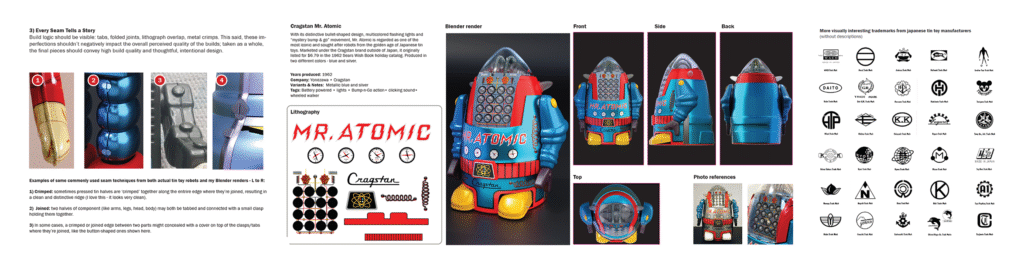
– A visual archive of my previous robot creations — with views, lithography, and photos of the real bots they were based on
– A Principles and Art Direction “bible” outlining my design philosophy and a shared glossary of terms
– A catalog of tin robot box art, broken down by style and features — a visual taxonomy of packaging tropes
– A collection of vintage brand logos from Japan’s classic tin toy makers
– A “special edition” brief focused on plastic robots that emerged in the 1970s, after the tin era began to fade
I made a set of design briefs — including principles and art direction, my Blender robot designs, box art styles, and branding — and uploaded them to my custom GPT’s knowledge base.
Building a Shared Language: The Taxonomy Phase
To preview the results now that the design briefs were in place, I described some random robot styles and themes, and put Gizmo to the test. I was pleased with even the earliest results, but soon realized I couldn’t just keep making robots one by one; my prompts were too ustructured and random. I needed to define the rules of the road: what were the recurring patterns, silhouettes, joints, litho treatments, and mechanical moods that defined these bots? And where could I stretch them?
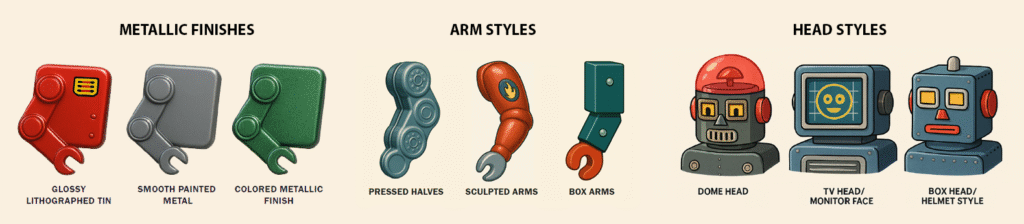
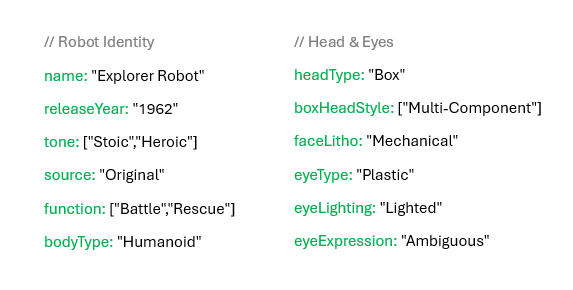
So Gizmo and I got to work categorizing. Together, we broke robots down by everything from tone and function (Was it stoic? Companion-based? Rescue-focused?) to body type, head type, lithography density, joint construction, even the style of “eye expression.” What emerged was a creative taxonomy; not a rigid system, but a modular language that made sense of my fictional lineup.
Classic tin bots helped too. Mr. Atomic, Thunder Robot, Target Robot, the Cragstan Astronaut – each contributed DNA to the system. We “stress tested” our learnings by naming some of these famous robots and asking how we might define them based on our evolving taxonomy. That process further clarified the shared rules: the design logic that made a 1960s Japanese toy feel like part of a greater whole.
The taxonomy we developed accounted for a variety of tin toy robot characteristics, including finish type and stylistic options for various body parts.
Formalizing the Process: The SpecBuilder App
While we were still developing the taxonomy, I noticed Gizmo was already turning my informal descriptions into clean, ready-to-use spec sheets, the kind I could drop into a prompt to generate an image. On a lark, I said, “Wow, it’d be awesome if we had an app with dropdowns and fields where we could just plug in a robot’s traits and get an organized spec sheet like this.”, to which Gizmo replied: “Actually, we can! Let’s build it.” And just like that, SpecBuilder was born.
My coding skills are pretty minimal; sure, I can prototype my way out of a wet paper bag and tinker with CSS to tweak a blog layout, but building a full React tool for robot design seemed way outside my comfort zone. So I asked Gizmo to walk me through the process in the tiniest baby steps, as if we were following LEGO instructions or building IKEA furniture step-by-step.
We spent an afternoon setting my computer up with Visual Studio Code and plugging in clean scripts Gizmo generated based on our feature set: selecting attributes, exporting spec sheets, clearing fields to start fresh. It came together faster than I imagined.
The Power of AI as a Creative Partner
By this point, I’d long stopped thinking of Gizmo as just an image generator or code helper, but more of a collaborator. Thanks to this very new partnership, we were already transforming some of my loosely defined concepts into tangible artifacts in an iterative, reciprocal way, often leading me to discoveries beyond anything I imagined when I first started this project. I’m less hung up than before about defining the boundaries between artist and AI, and leaning in to embrace its undeniable strengths: faster iteration, clearer feedback loops, and a thought partner who never gets tired. But the ideas, logic and visual coherence are all still very much on me. And that’s exactly how I want it.
What’s Next: The Expanded Universe
SpecBuilder is now at a place where I can generate fully spec’d robot concepts in minutes, ready to import into Blender as templates for my 3D designs. Next up is testing it against real and imagined designs, building boxes to accompany them, adding more visual logic to the app, and eventually expanding to include vehicles and modular companion bots. (We’re also still working through some styling quirks related to Tailwind; nothing showstopping, just another step in the polishing process.)
I don’t know if this is a toy catalog, an alternative reality, or just goofing off – maybe it’s all the above. But so far it’s been creatively satisfying in a way few projects have been. It lets me explore this gap between my own personal nostalgia and invention, and build a world that feels like it could’ve been stocked on a shelf in 1964, right between Mr. Atomic and Super Astronaut.